Financial Technology, or Fintech, encapsulates the revolutionary synergy between finance and technology, reshaping the traditional landscape of financial services.
In essence, Fintech represents the innovative use of technology to enhance and streamline various financial activities, from banking and payments to investment and insurance.
This blog will explore the dynamic evolution of technology within the financial sector, tracing its transformative journey over the years.
From the early days of computerization to the current era of advanced algorithms and blockchain, the financial industry has undergone a remarkable metamorphosis.
According to EMR, In 2023, Global Fintech Market was valued at 226.76 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.8% and will be valued at around USD 917.17 billion by 2032.
1. Digital Banking as New Technology in Finance
Online banking platforms
Digital banking stands at the forefront of the financial technology revolution, ushering in a new era of convenience and accessibility.
Online banking platforms have become synonymous with the modern banking experience, offering customers a seamless and efficient way to manage their finances.
At the forefront are mobile banking apps, providing users with the power to conduct transactions, check balances, and even engage in investment activities at their fingertips.
Simultaneously, internet banking portals offer a robust online interface for a comprehensive range of financial services, empowering users to handle everything from bill payments to account management with ease.
The integration of these technologies not only simplifies daily financial tasks but also enhances the overall customer experience, marking a significant paradigm shift in the way individuals interact with and control their financial resources.
Digital wallets and payment systems
Digital wallets and payment systems have redefined the way we handle transactions, introducing unparalleled convenience and security.
According to Statistica, The Digital Payments Market will grow to 5,480m users by 2027. And in 2024 The Digital Assets market is expected to show a revenue growth of 33.1%.
Contactless payments, a hallmark of modern finance, enable swift and secure transactions with a simple tap or wave, eliminating the need for physical cards. Peer-to-peer transactions, facilitated by digital wallets, empower users to seamlessly send and receive funds directly from their smartphones.
This technology not only enhances speed but also prioritizes safety through encrypted transactions. The integration of contactless payments and peer-to-peer transactions represents a dynamic shift toward a cashless society, offering users efficient and flexible financial solutions in an increasingly digital world.
2. Applications of AI in Financial Decision-Making
AI in Finance has become a pivotal force in reshaping the landscape of financial technology, particularly in the realm of fraud detection and prevention.
AI-powered anomaly detection algorithms scrutinize vast datasets to identify irregular patterns indicative of fraudulent activities, offering a proactive defense against potential threats.
Concurrently, the integration of behavioral biometrics leverages machine learning to analyze unique user patterns, such as keystroke dynamics or mouse movements, enhancing authentication processes and fortifying the security of financial transactions.
This fusion of AI and ML not only bolsters the financial sector’s resilience against fraud but also ensures a more nuanced and adaptive approach to security, staying ahead of evolving threats in the ever-changing digital landscape.
As financial institutions harness the potential of AI and ML, the future promises a more secure, efficient, and technologically advanced financial ecosystem.
Credit scoring and risk assessment
In the realm of credit scoring and risk assessment, the integration of technology, specifically through automated credit decisions and predictive analytics, has revolutionized traditional processes.
Automated credit employs algorithms to swiftly analyze an individual’s creditworthiness, facilitating faster and more accurate lending decisions.
Predictive analytics leverages advanced statistical models to assess future risks, providing financial institutions with valuable insights into a borrower’s repayment behavior.
These technological advancements not only streamline the lending process but also enhance the precision of risk assessment, allowing financial institutions to make data-driven decisions and better manage potential credit risks in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
3.Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology, a decentralized and distributed ledger, forms the foundation for transformative innovations in finance. Its core strength lies in providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record of transactions across a network of computers.
In the realm of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin and Ethereum stand out as major players, utilizing blockchain to enable peer-to-peer transactions, and fostering financial autonomy. Beyond transactions, Ethereum introduces smart contracts, self-executing contracts with coded terms, enhancing automation and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) further leverages blockchain, allowing users to engage in traditional financial activities like lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional intermediaries.
This decentralized model challenges traditional financial systems, offering efficiency, accessibility, and financial inclusion. As cryptocurrencies and blockchain continue to evolve, their impact on finance extends far beyond digital currencies, shaping the future of decentralized and democratized financial ecosystems.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Finance
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is reshaping the landscape of financial operations, particularly in the realm of back-office processes. By automating labor-intensive tasks, RPA enhances efficiency and accuracy in financial workflows.
In back-office operations, RPA excels in tasks such as data entry and reconciliation, reducing the potential for errors and expediting traditionally time-consuming processes. Through process automation, RPA tackles routine and rule-based functions, allowing human resources to focus on more strategic and complex aspects of financial management.
This transformative technology not only accelerates task completion but also ensures consistent and error-free execution of financial processes.
As financial institutions increasingly adopt RPA, its potential to streamline back-office operations heralds a new era of productivity and precision in the financial sector, ultimately contributing to enhanced service delivery and operational excellence.
5. RegTech: Technology for Regulatory Compliance in the Finance Industry
RegTech, an amalgamation of “regulatory technology,” emerges as a crucial ally for financial institutions grappling with the complexities of regulatory compliance.
In navigating the intricate regulatory landscape, technology becomes a guiding force. Compliance automation and reporting tools, integral components of RegTech, facilitate seamless adherence to regulatory requirements by automating processes like reporting, monitoring, and risk assessment.
The benefits of RegTech are manifold, significantly reducing compliance costs and mitigating risks associated with non-compliance. By leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and data analytics, RegTech not only ensures accuracy and efficiency in compliance tasks but also enhances the agility of financial institutions in adapting to evolving regulatory frameworks.
In an era where regulatory demands are ever-expanding, RegTech stands as a strategic imperative, empowering the finance industry to uphold compliance standards while fostering innovation and operational resilience.
6. Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms have emerged as disruptive forces, challenging traditional lending models and revolutionizing the way individuals and businesses access financing.
By directly connecting borrowers with lenders through online platforms, P2P lending eliminates the need for traditional financial intermediaries, fostering a more streamlined and efficient lending process.
The disruption of traditional lending models is evident in the democratization of finance facilitated by P2P platforms. These platforms offer an alternative to traditional banking, providing borrowers with access to capital outside the confines of established financial institutions. This democratization, however, introduces new challenges related to risk and regulation.
As P2P lending grows, ensuring the security of transactions, protecting investors, and maintaining market integrity become paramount concerns. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to strike a balance between encouraging innovation and safeguarding the interests of all stakeholders.
Despite these challenges, P2P lending has made significant strides in promoting financial inclusion. By catering to underserved individuals and businesses often overlooked by traditional banks, P2P lending platforms bridge gaps in access to credit.
This inclusive approach empowers a broader spectrum of borrowers, fostering economic participation and growth. As P2P lending continues to evolve, navigating risks and adapting regulatory frameworks will be crucial to sustaining its positive impact on financial inclusion.
Fintech Regulations and Technology
Navigating the regulatory landscape is a critical aspect of the fintech sector, where innovation and compliance intersect. Fintech regulations present unique challenges, particularly as technology evolves at a rapid pace.
Compliance challenges arise from the need to align innovative solutions with existing regulatory frameworks, often designed for traditional financial models. Fintech firms must grapple with the complexities of adapting to and meeting these regulatory requirements while maintaining their commitment to innovation.
Globally, regulatory frameworks for fintech vary, reflecting diverse approaches to managing the sector’s growth. Some regions have embraced a proactive stance, fostering innovation through supportive policies, while others adopt a more cautious approach to mitigate potential risks.
Striking the right balance between encouraging fintech innovation and implementing safeguards to protect consumers, investors, and the financial system is a global challenge. Collaborative efforts between regulators, industry players, and policymakers are essential to develop frameworks that promote responsible innovation while addressing emerging risks.
As fintech becomes increasingly integrated into traditional financial systems, the regulatory landscape will continue to evolve. Finding a harmonious balance between innovation and risk mitigation remains a dynamic challenge, requiring ongoing dialogue and adaptability to ensure the long-term sustainability and integrity of the fintech ecosystem.
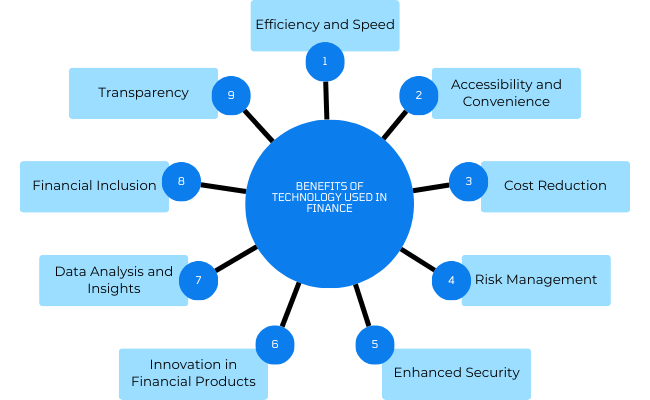
Benefits of Technology Used in Finance
Efficiency and Speed
Technology in finance streamlines processes, reducing manual efforts and increasing the speed of transactions, data processing, and decision-making. This efficiency leads to quicker and more accurate financial operations.
Accessibility and Convenience
Online banking, mobile apps, and digital financial platforms make it easier for individuals and businesses to access their financial information anytime, anywhere. This accessibility enhances overall convenience and empowers users to manage their finances on the go.
Cost Reduction
Automated processes and digital solutions often result in cost savings for financial institutions. Tasks that once required significant manpower can now be executed more efficiently with technology, reducing operational expenses.
Risk Management
Advanced analytics and algorithms help in assessing and managing financial risks more effectively. Technology enables real-time monitoring of market trends and potential risks, allowing for proactive risk management strategies.
Enhanced Security
With the use of encryption, biometrics, and secure authentication methods, technology has significantly improved the security of financial transactions and data. This helps in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and fraudulent activities.
Innovation in Financial Products
Technology has driven innovation in financial products and services, leading to the development of new investment options, payment methods, and lending solutions. This innovation expands choices for consumers and promotes a more dynamic financial landscape.
Data Analysis and Insights
Big data analytics and artificial intelligence enable financial institutions to analyze vast amounts of data to gain valuable insights. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making processes, allowing for more informed strategies and personalized services.
Financial Inclusion
Technology has played a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by providing banking services to underserved populations. Mobile banking and digital wallets have made it easier for people in remote areas to access basic financial services.
Transparency
Blockchain technology, in particular, enhances transparency in financial transactions. It provides a secure and decentralized ledger that reduces the risk of fraud and ensures that financial records are accurate and tamper-proof.
Global Connectivity
Technology has facilitated global connectivity in the financial sector, allowing for seamless cross-border transactions, international investments, and collaborations. This interconnectedness contributes to the globalization of financial markets.
Challenges and Risks of Technology in Finance
The integration of technology in finance has undoubtedly transformed the industry, but it also brings about a set of challenges and risks that demand careful consideration. Here’s an exploration of some of the key challenges and risks associated with technology in finance:
Cybersecurity Threats
The challenge lies in the growing dependence on digital platforms, exposing financial institutions to heightened cyber threats. This poses a significant risk, as potential breaches, data theft, and unauthorized access could compromise sensitive financial information, resulting in financial losses and reputational damage.
Regulatory Compliance
The rapid pace of technological progress surpasses regulatory frameworks, posing compliance challenges for financial institutions and fintech firms.
Non-compliance risks legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage. Achieving a delicate balance between innovation and adherence to evolving regulatory standards remains a persistent challenge in the financial technology landscape.
Data Privacy Concerns:
The challenge arises from collecting and using extensive customer data, prompting concerns about privacy and ethical use. Mishandling such information poses risks of legal repercussions, eroding customer trust, and inviting regulatory sanctions. Safeguarding privacy while utilizing data responsibly remains a critical task in the evolving landscape of technology in finance.
Operational Disruptions:
Relying on intricate technological systems heightens the risk of operational disruptions from system failures, software glitches, or cyberattacks. These disruptions can result in financial losses and negatively impact customer service, underscoring the importance of robust and resilient technological infrastructure in the financial sector.
Dependency on Third-Party Providers:
The challenge lies in financial institutions’ dependence on third-party technology providers for critical services. The associated risk involves potential disruptions or failures in these third-party systems, leading to service interruptions and impacting the seamless functioning of financial operations.
Mitigating such dependencies becomes crucial for ensuring operational continuity in the financial sector.
Conclusion
The financial landscape is undergoing a profound metamorphosis propelled by key technologies that redefine how we perceive, interact with, and manage financial resources.
From blockchain and artificial intelligence to digital payments and RegTech, each innovation contributes to a more efficient, accessible, and secure financial ecosystem.
These transformative technologies not only enhance operational processes but also introduce novel solutions like decentralized finance and smart contracts.
Looking forward, the ongoing and future implications of technology in finance emphasize the need for continuous adaptation. Failing to embrace technological advancements could mean missing out on efficiency gains, competitive advantages, and the ability to navigate evolving regulatory landscapes.
Therefore, the importance of proactively integrating and adapting to these technological shifts becomes paramount for sustained success in the financial industry.
As the industry continues its digital evolution, those agile enough to harness these innovations will undoubtedly thrive in the dynamic and technologically driven future of finance.