You might have heard this term many times in your school days from your teacher while explaining Biology chapters- Animal Kingdom. If you’ve focused on your class, you must know the meaning of Amphibians and their characteristics. If you have skipped this chapter and now want to learn the meaning of Amphibians, this post is for you. We will bring a clear description of this term and all possible information related to this to make you understand deeply. Also, we will elaborate on the classifications of Amphibians so that you won’t be left with an unclear point.
Let’s start with a simple and easy-to-understand description of the Amphibian.
What is Amphibian?
An amphibian is a class of animals that can exploit both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. The word Amphibian is derived from the Greek – Amphibious- living dual life. Amphibians reflect dual life strategy, though some are permanent land dwellers, while other species live completely on aquatic mode.
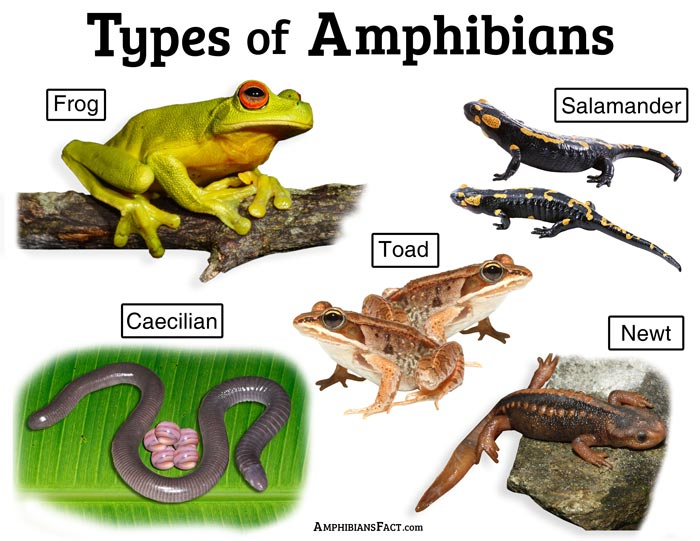
Approximately 8,100 species of amphibians are known, and frogs & toads are the most recognizable ones. Today, amphibians are divided into three orders: Anurans (Frogs and Toads), Urodela (Salamanders and Newts), and Gymnophiona (Caecilians). These three living amphibians are thought to have derived from a single radiation of an ancient amphibian. Still different in body structure, they are probably the closest relative to each other. They can’t be called Synapomorphy because of different body forms.
Frogs are the most recognizable and certainly the most abundant members of the class of animals known as amphibians. But frogs and toads are not the only members of this group. We will mention other members of this group later in this post. We have mentioned frogs as an example because you may have caught frogs in nearby ponds in the summertime as a child. It was the best example to describe the meaning of amphibian.
Amphibians (Class of animals) belong to the Phylum Chordata, which simply means animals in the Chordata Phylum have a backbone. Let’s take a closer look at the details of Amphibians.
Character of Amphibians
The characteristics of Amphibians are described as follows. Read the below details carefully and clear your doubts.
- Amphibians can live both in or out of water.
- Their body is divided into head or trunk, the tail may or may not be present.
- Amphibians are found in warm environments that is why they are called Ectothermic animals.
- They usually have two pairs of limbs for locomotion.
- The other characteristic that defines amphibians is they breathe through lungs and skin. Gills present barely in some adults.
- The fertilization is external in two orders, while in Salamanders, the fertilization is internal.
- The heart of Amphibian is three-chambered.
- Examples- Frog, Toad, Ectotherm, Crocodile, etc.
- They typically have moist and smooth skin.
- They have no paired fins, but unpaired fins might be there.
These are the characteristics of amphibians that differentiate them from other classes of animals. Now, go through the in-depth details of classifications of Amphibians that we have mentioned above.
Classifications of Amphibian
Amphibians are divided into three orders. Check the details below.
Apoda (Gymnophiona or Caecilia)
- They have no legs and are also known as ‘blind worms’ because their eyes are covered by skin or bone.
- They possess venom glands.
- They secrete mucus to reduce water loss.
Urodela (Caudata)
- Their fertilization is internal.
- They have long tails.
- The skin of these organisms is smooth with poison glands.
- There is a little difference between males and females.
- They have hidden gills.
- They are found under leaf litter, in the soil, or water.
- They eat insects and worms.
Anura(Frogs, Toads, and Salientia)
- There are around 3400 species of this order in the world.
- Animals of this order have four limbs.
- The head and trunk of animals related to this order are fused.
- Fertilization of this classification is external and the eggs are laid in water. Eg, frogs, and toads.
If you want more relevant information, leave a comment. We will be back with another post soon.